In the realm of web development, you may hear frequent references to redirects, and you may be wondering, “What are redirects?” This guide provides insight to allow you to better understand redirects and their importance.
What is a redirect?
A redirect is a way to send both users and search engines to a URL that is different from the one that was originally requested. In other words, you are redirecting the user or search engine from one URL to another.
When are redirects used, and why is it important to use them?
| Deleted Page |
Commonly, redirects are used in instances where the URL that was requested has either been removed or contained content that is no longer relevant to the overall goal of the website. Therefore, a redirect serves the purpose of leading a user or search engine towards a page that is either a new version of that page, a page that has similar content that is more relevant to the website, or any other page that the website administrator would prefer for the user or search engine to land on. |
| Changed URL |
Another instance where a redirect is used is when the URL of a page is changed. A URL may be changed in an effort to boost the search engine optimization (SEO) of a page by either including keywords relevant to the content, separating words with hyphens, avoiding filler words like “a” or “the”, to provide a few examples. When a URL is changed, redirects ensure that even if the old URL exists elsewhere, users and search engines are sent to the correct URL and are able to view the intended content. |
| Changed Parent Page |
Redirects are relevant when the page’s parent has been changed, therefore changing the URL structure. For example, if we were to change the parent page of www.newmediacampaigns.com/services/branding-design from Services to Blog, we would want to redirect the original URL to www.newmediacampaigns.com/blog/branding-design to both reflect that change and ensure that users and search engines are being sent to the new URL. |
| Website Moved to a New Domain |
When a website is moved to a new domain, or a new, updated version of your site is built under a new domain, the URL structure of every page on that website will change to reflect the new domain. When that occurs, you’ll want to be sure to put 301 redirects in place to send users and search engines that request a URL with the old domain to one with the new domain. For example, the 301 redirects would send users who requested www.oldmediacampaigns.com/blog to the new domain at www.newmediacampaigns.com/blog and present to the user the content they were intending on viewing. This will help to avoid 404 errors when instances such as an old URL existing on the new site or on an external site occurs. |
| New Website Built Under the Same Domain |
Though you may not see the use for redirects if your new website has the same domain as the old one, redirects are quite crucial in this case. Often, when a new website is built, new language is used to refer to different areas of the site, changing the URL structure. For example, “Blog” may be changed to “Insights” or “Our Staff” may be changed to “Meet the Team”. In this case, the URL has changed to reflect the new language and title of the pages. To ensure that users are being sent to the page they are requesting, you will want to put redirects in place that reflect this change in language. For example, if we were to redesign and rebuild our website under the same domain, but change “Blog” to “Insights”, we would want to redirect https://www.newmediacampaigns.com/blog to https://www.newmediacampaigns.com/insights to reflect the new language used and make sure that users are sent to the new page rather than encountering a 404 error. |
| Performing Maintenence on a Webpage |
When you are performing maintenance on a webpage, you should put a temporary redirect in place. When this is done, users and search engines are able to be sent to a page that has content relevant to the page that they were requesting and/or an active page explaining why the page they requested is not available, rather than receiving a 404 error. When users receive 404 errors, they are less likely to revisit your site as a whole and are more likely to bounce from your site, negatively affecting SEO via low user engagement. Additionally, when search engines encounter an error from a page not actively existing, SEO is negatively affected as the search engine will avoid showing sites with broken or unavailable pages to users. |
| Merging Duplicate Pages |
When your site has duplicate pages, it is often in good practice to merge them into one. This improves SEO by avoiding a situation where traffic to one page is being cannibalized by another when one of the duplicates is visited more than its counterpart. When redirects are in place to lead users from one of the duplicate pages to the new merged page, search engines will know to present that page as the search result rather than multiple pages with the same content, therefore increasing the amount of traffic to a single page. As traffic increases to a page, so does its search engine ranking, meaning you are likely to have a page rank higher in search results when there is only one version of it on your site. |
Domain Forwarding
There are a few reasons why someone may implement a domain redirect, also known as domain forwarding: maybe you rebranded and changed the name of your business or organization, or you own multiple domains that are similar or relevant to your site and would like to ensure that a URL featuring any one of those domains leads to your primary domain. Just like how URL redirects send users and search engines from the requested URL to the correct URL, domain redirects serve to send users and search engines from the requested domain to the primary domain.
Domain redirects are important for many of the same reasons that URL redirects are:
- Maintain the SEO value of an existing site while passing the site to a new domain
- Promote search result rankings for your primary site by ensuring all of the content relevant to your business or organization exists in one place
- Ensure an enjoyable user experience by decreasing the likelihood of a user running into a 404 error via an old/unused domain
In order to ensure that search engines know where to find your content in its new location, you should put a 301 redirect in place. When this is done, search engines will act as though the old or alternate domain no longer exists, and will send itself and users towards URLs with the new domain. This will assist in upholding the status of your search engine rankings as well as maintaining your traffic as search engines and users will crawl and view the intended content, the only difference is that now it is under a new domain.
Best Practices for Domain Forwarding
- Check Your New Domain: Ensure that your new domain has not been previously penalized by search engines for either poor SEO practices or having been used for spam. To do this, use Google Search Console and check the Manual Actions report under Security & Manual Actions. From there, you will be able to see if there are no outstanding penalties on your site, and if there are, how you can fix them. Once the changes are made, you can submit a request for Google to reconsider the penalty, which they will then tell you if the penalty has been removed.
- Backup Your Site: To safely make sure that you have access to all content that you want to keep from the previous domain, you should backup all files and databases on a domain. This way, you are able to confidently move from one domain to another without the fear of losing crucial or important content. You can find a guide outlining how to successfully backup your site here.
- Transfer Content to the New Domain: If your site is small, there’s a possibility that you can manually transfer content. For example, ronwilliams.net, a site we recently redesigned and launched, was small enough to where all of the content from the old site was manually uploaded to the new site. This is also a great way to audit the content on your small site and ensure there aren’t duplicate pages and to see if there is content at the old domain that you will no longer need or prefer not to have on the new domain. However, in cases where you are unable to manually upload the new content, you will need to transfer your files from the backup to your new domain. There are many different ways to do this, so we recommend checking in with your development team or CMS provider to gather insight regarding the best (and easiest) way to complete this task.
- Notify Search Engines of the Domain Move: To ensure that Google knows that your domain has moved, you’ll want to log in to your Google Search Console and verify the new domain. From there, you’ll navigate to the Settings, choose Change of Address, and follow the instructions provided. Here is a guide that outlines this process.
- Check the New Site for Old Links: After the domain forwarding is complete, and once your old domain is shut down, any internal links on your site that are not redirected will result in a 404 error. From there, you should take note of those links and where they are meant to lead to and add the 301 URL redirects to your site to point them to the proper location. You should also keep an eye on Google Search Console within the first few days/weeks after your new domain is launched and take note of any 404 errors flagged in the Indexing section of the console. You can then implement redirects based on which page under the new domain the broken URL is meant to lead to.
What are the main types of redirects?
There are several different types of redirects, but there are two that are primarily used - 301: Moved Permanently, and 302: Moved Temporarily.
| 301 | 302 |
|
|
Why are redirects important for SEO?
Redirects are crucial when it comes to Search Engine Optimization (SEO) for several reasons, ranging from page indexing to user experience.
Page Indexing
Redirects are your way of telling search engines that content on a site has been moved, where it was moved to, and if that move is permanent or temporary. Without redirects, search engines will attempt to crawl URLs that no longer contain content, which will lead to your site being deemed as unreliable or neglected as the search engine encounters 404 errors. This will result in your site placing lower in search engine rankings, decreasing the amount of Organic traffic your site receives.
User Experience
When users encounter a 404 error, indicating that the URL and content they were requesting cannot be found, they are likely to bounce from your site and/or not visit your site again in the future. Redirects assist in retaining users on your site as a redirect will send users to the correct URL from the one that they were requesting, allowing them to view the content they are intending to view. When users spend more time on your site (an engaged session) or are repeat visitors of your site, search engines will pick up on this increase of legitimate traffic and, as a result, place your site higher in search engine rankings. As your site rises in search engine rankings, more users are likely to visit your site, continually increasing traffic and therefore continually improving your search engine rankings.
SEO is important in every realm amongst many different industries, such as website design for nonprofits and law firm website design, and redirects are just one step to take in ensuring that you are doing everything you can to attract visitors. Google Analytics is a great tool to track how your SEO improvement efforts are affecting your site traffic, and can provide benefical insight regarding the behaviors of users on your site. This can help you to determine how redirects may assist certain goals your organization has in mind, such as choosing to redirect users to a certain landing page in order to foster certain conversions or promote a prioritized campaign. Discover more SEO tips and information on our Marketing blog!
What are some best practices that I should keep in mind when implementing redirects?
Always Redirect to Similar Content
When redirecting, always ensure that the page that the redirect is targeting contains content that is similar to the requested URL. Not only will it ensure that the page and its content are relevant within search results, but will also ensure a positive user experience. When a user is intending on viewing one type of content but is sent to a page that contains a different type of content, they are likely to unhappily bounce from your site to another, negatively affecting traffic, user engagement times, and therefore the SEO and search engine ranking of your site.
Avoid Redirect Chains
When there is more than one step between the original URL and the final URL, a redirect chain exists. In other words, if you redirect URL A to URL B, and then URL B to URL C, you have a redirect chain. Not only is this complex in general, but can delay your site being crawled by search engines as well as increasing the load time of your page, both of which can negatively affect user experience and SEO. Instead, you should set URL A to redirect straight to URL C.
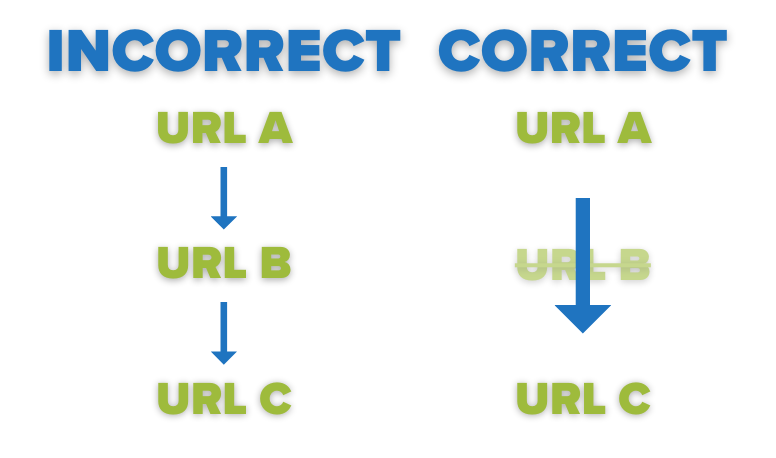
Avoid Redirect Loops
When URL A redirects to URL B, and then URL B redirects back to URL A, a redirect loop occurs. When this happens, the site is attempting to redirect URL B to URL A, but the redirect put in place at URL A is telling the site to send users to URL B, causing confusion. This may happen when someone has forgotten about the redirect that is already put in place, or if a 301 redirect (moved permanently) rather than a 302 redirect (moved temporarily) was put in place while URL A was being maintenanced. This results in an error, keeping users and search engines from reaching their requested URL. As we know, this negatively affects user experience and SEO. To avoid this, find the correct redirect (in this case, URL B to URL A), and delete the incorrect/no longer applicable redirect (in this case, URL A back to URL B.
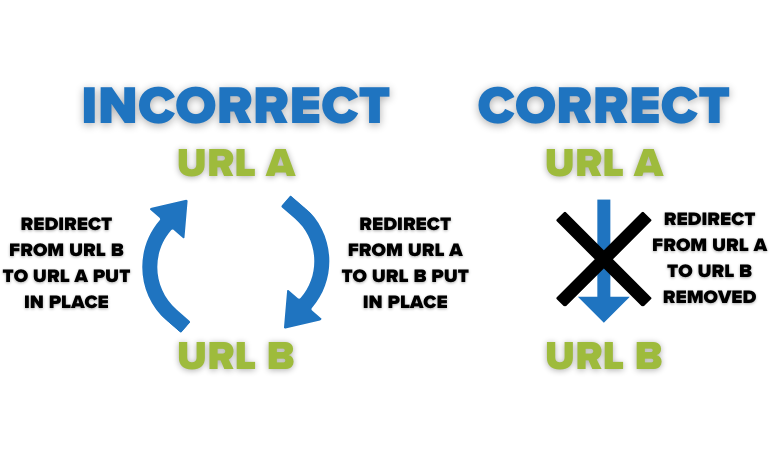
Replace Old Links on Your Site with the New Link
In other words, ensure that there are not any areas of your site that link to a page with a redirect. When this exists, users will still be redirected properly. However, it may take longer than if they were directly sent to the new page and can potentially result in a redirect chain as time goes on and more redirects are put in place. Doing regular checks and redirect maintenance on your site is extremely helpful in ensuring that your users have a seamless experience and that your site is SEO friendly.
All in all, redirects are crucial for ensuring that users and search engines are able to view and crawl the intended content when attempting to visit the requested URL. When redirects are in place, search engines and users are pleased as they are able to note that your website is legitimate, provides relevant and intended content, and is not neglected. When search engines and users are pleased, SEO is improved, search engine rankings are boosted, and more traffic is drawn to your site; all things that, when put together, help to make for a successful website!



Leave the first comment